Developing a writing research proposal is a core ability for engineering students and working engineers. A properly developed proposal not only explains a subject but convinces the reviewers of its relevance and applicability. This literature review article will provide you with a road map that will guide you in writing a good research proposal.
Step 1: Understand the Requirements
1.1 Review Guidelines
Before one can begin to write, he or she should go through points given by the funding body or institution. Be sure to follow format requirement, word count, and submission date.
1.2 Identify Key Components
Most research proposals require:
Title
Abstract
Introduction
Literature Review
Methodology
Expected Outcomes
Timeline
Budget (if applicable)
References
Step 2: Choose a Relevant Topic
2.1 Identify Your Interests
Carefully analyze your specialization areas within the engineering discipline. This is where your passion for the topic realizes itself in the proposal.
2.2 Address Real-World Problems
Look at the current engineering problem or; enhance already existing technologies. Linking your proposal up with what the industry requires enhances its quality.
Step 3: Conduct a Literature Review
3.1 Survey Existing Research
Related: Read published work to get exposed to what is currently known about the problem. This is assist in discovering holes that your project can fill.
3.2 Cite Recent Studies
Cite recent articles to let your examiner know your ways of thinking and set context before proposing your ideas.
Step 4: Write the Proposal
4.1 Craft a Compelling Title
Select title that can easily be understood and relevant to the project’s objective. Thus, a good title makes the reader interested in the article and briefly describes the direction of the investigations.
4.2 Holding the Audience’s Interest through an Interesting Abstract
The abstract of the paper should be similar to your proposal and should not be more than 250 words or below 150 words. This is the key proposal documents and should include the research question, a rationale for the study and the method of research and expected findings.
4.3 An introduction to your research problem
In economics, describe the area or gap in knowledge that your study intends to explore. Describe why it is important or of interest and why it should be studied.
4.4 elaborate Your Literature Review
Explain the points of similarities and differences between past research and your research study.
4.5 Describe Your Methodology
Explain the techniques that will be used in the study. Be specific about:
Data collection techniques
Experimental design
Analysis methods
Procured and used in any of the accessible phases Dingle, P. (1997). Open Mind and Active Voice: Information Literacy, Media and Learning in the New Millennium. Dublin: Ailing.
4.6 Discuss Expected Outcomes
Explain the possible implication of this research. What new development will it foster in the field? In what way could it affect industry practice?
4.7 Provide a Timeline
Release a sound working timetable that defines at least five phases of the project development starting from research phase to the phase of analysis. This an indication that you are professional that has considered the practicalities.
4.8 If necessary, you are required to draw an outline of your budget
Include a detailed budget if any was done If the above cost is too detailed, indicate that a detailed budget was prepared where necessary. Estimate the cost of resources such as the material and equipment used for the project as well as the workers your actual expense estimates have to be reasonable and could be explained.
Step 5: Review and Edit
5.1 Seek Feedback
Discuss your proposal with classmates, colleagues or professors. Receiving or giving constructive criticism can go a long way in sharpening your mind and the way you present ideas.
5.2 Revisions for Clarity and Clarity
Do not use any technical language or any form of informal language in your writing either. Intrinsic considerations of precision and concision shall improve the text’s legibility.
5.3 Proofread
Look for point forms and punctuation. Polished is the last thing before submitting the proposal so that there will be a very high sense of professional and polished neatness of the proposal documents.
Step 6: Prepare for Submission
6.1 Format 65 According to Guidelines
Check how much your proposal meets all the formatting requirements. This involves issues such as writing font size, margins and style of citation amongst others.
6.2 Make sure of submission requirements
Make sure that you have had all the components called for and ensure that you have complied with any special submission requirements.
6.3 Submit on Time
A plan especially one developed in advance can help avert problems that may occur. It is always good to submit your proposal much earlier than required time in case of any emergent situation.
Additional Tips for Success
Tailor Your Proposal: Try to align the content with that which the users are expecting to find on your website or use.
Use Visuals: Use additional charts or diagrams in the case when the message is more detailed and might be quite confusing.
Be Concise: Stick to the issue, do not use professional terms that will make the reader influenced to another without grasping the point.

 Workshop on Embedded Systems: Building Real-World Applications
Workshop on Embedded Systems: Building Real-World Applications  Top Internship Training & Certificate
Top Internship Training & Certificate  Internship Benefits Beyond the Resume: How It Shapes Your Career
Internship Benefits Beyond the Resume: How It Shapes Your Career  Turing Internship into Job Offers: Strategies for Success
Turing Internship into Job Offers: Strategies for Success  Day in the Life: A Glimpse into the Realities of Internship Experience
Day in the Life: A Glimpse into the Realities of Internship Experience  Internship Insights: What Recruiters Look for in Candidates
Internship Insights: What Recruiters Look for in Candidates  Why Internships Matter: Building Bridges to Your Future Career
Why Internships Matter: Building Bridges to Your Future Career  Smart Mirror Based on Raspberry Pi
Smart Mirror Based on Raspberry Pi  Best Major & Mini Project Ideas for Engineering College Students
Best Major & Mini Project Ideas for Engineering College Students  Top B.Tech/M.Tech Engineering Projects Consultants & Services
Top B.Tech/M.Tech Engineering Projects Consultants & Services  Engineering Project Ideas & Topics for Students
Engineering Project Ideas & Topics for Students  Engineering Procurement Construction (EPC) Project Services: Step By Step Guide
Engineering Procurement Construction (EPC) Project Services: Step By Step Guide  IEEE Projects in Tirupati
IEEE Projects in Tirupati  Simple Mini Project Ideas for Engineering Students
Simple Mini Project Ideas for Engineering Students  Project Center in Tirupati
Project Center in Tirupati  Top Engineering Project Consultants in Tirupati
Top Engineering Project Consultants in Tirupati  Innovative Software Engineering Projects: Shaping the Future of Technology
Innovative Software Engineering Projects: Shaping the Future of Technology  Major Current and Upcoming Projects
Major Current and Upcoming Projects  Best Project Management Consultant in Tirupati
Best Project Management Consultant in Tirupati  Top 10 Best Project Consultants in Andhra Pradesh
Top 10 Best Project Consultants in Andhra Pradesh  Best Project Consultancy in Tirupati
Best Project Consultancy in Tirupati  Advanced Technology Project Ideas in Chittoor
Advanced Technology Project Ideas in Chittoor  Top Final Year Project Provider in Tirupati
Top Final Year Project Provider in Tirupati  Mini and Major Projects in Chittoor
Mini and Major Projects in Chittoor  Final Year Projects in Tirupati: Unlocking Your Academic Potential
Final Year Projects in Tirupati: Unlocking Your Academic Potential  Affordable Academic Projects in India: A Gateway to Success
Affordable Academic Projects in India: A Gateway to Success  Trending Engineering Project Ideas in Tirupati 2025
Trending Engineering Project Ideas in Tirupati 2025  Technical Project ideas for engineering students
Technical Project ideas for engineering students  How Do I Choose A Project Topic Titles For Final Year Engineering Students?
How Do I Choose A Project Topic Titles For Final Year Engineering Students?  Find Best College Project Centers in Andhra Pradesh
Find Best College Project Centers in Andhra Pradesh  Latest Engineering Project Ideas for 2025
Latest Engineering Project Ideas for 2025  Top Engineering Project Work in Vizianagaram: Empowering Student Success
Top Engineering Project Work in Vizianagaram: Empowering Student Success  Final Year Project Ideas for Students in Chittoor
Final Year Project Ideas for Students in Chittoor  Project Ideas for College Students in Telangana
Project Ideas for College Students in Telangana  Top 10 Mini Project Ideas for College Students
Top 10 Mini Project Ideas for College Students  Project Work for Students in Tirupati
Project Work for Students in Tirupati  Best Engineering Projects in Andhra Pradesh: A Comprehensive Guide
Best Engineering Projects in Andhra Pradesh: A Comprehensive Guide  Using Cloud-Based Tools for Collaborative Research Projects
Using Cloud-Based Tools for Collaborative Research Projects  Advantages of Undergraduate Research Opportunities
Advantages of Undergraduate Research Opportunities  How to Prepare for Academic Research Conferences
How to Prepare for Academic Research Conferences  Understanding the Different Types of Academic Research
Understanding the Different Types of Academic Research  Navigating the Peer Review Process: Tips for Success
Navigating the Peer Review Process: Tips for Success  How to Write the Abstract for a Research Paper
How to Write the Abstract for a Research Paper  The Impact of Academic Research on Policy Making
The Impact of Academic Research on Policy Making  Exploring Open Access Journals for Academic Publishing
Exploring Open Access Journals for Academic Publishing  The Role of Academic Journals in Disseminating Research
The Role of Academic Journals in Disseminating Research  How to Balance Coursework and Research Projects: A Guide to Academic Success
How to Balance Coursework and Research Projects: A Guide to Academic Success  The Importance of Research Ethics Committees
The Importance of Research Ethics Committees  Innovative Teaching Methods to Support Academic Research Projects
Innovative Teaching Methods to Support Academic Research Projects  Creating Impactful Visual Aids for Research Presentations
Creating Impactful Visual Aids for Research Presentations  The Benefits of Peer Review in Academic Research
The Benefits of Peer Review in Academic Research  Surveys and Questionnaires are Effective in Academic Research
Surveys and Questionnaires are Effective in Academic Research  Importance of Documentation Record-Keeping in Academic Research
Importance of Documentation Record-Keeping in Academic Research  Overcoming Challenges in Academic Research Projects
Overcoming Challenges in Academic Research Projects  Leveraging Online Resources for Academic Research
Leveraging Online Resources for Academic Research  Successful Academic Projects in Computer Science: Case Studies
Successful Academic Projects in Computer Science: Case Studies  Building a Research Network: The Importance of Conferences and Workshops
Building a Research Network: The Importance of Conferences and Workshops  How Technology Affects Academic Research?
How Technology Affects Academic Research?  Getting Funding for Your Research Project: Tips and Resources
Getting Funding for Your Research Project: Tips and Resources  Time Management Strategies for Academic Researchers
Time Management Strategies for Academic Researchers  Ethical Considerations in Academic Research
Ethical Considerations in Academic Research  How to Write and Publishing Your Academic Paper?
How to Write and Publishing Your Academic Paper?  Presenting Your Research: Guidelines To Consider When Making An Academic Presentation
Presenting Your Research: Guidelines To Consider When Making An Academic Presentation  Analyzing Research Data: Effective Techniques in Engineering Projects
Analyzing Research Data: Effective Techniques in Engineering Projects  Best Practices for Conducting a Literature Review
Best Practices for Conducting a Literature Review  Project Management for Academic Research: Tools and Techniques
Project Management for Academic Research: Tools and Techniques  How to Choose the Perfect Academic Project Topic?
How to Choose the Perfect Academic Project Topic?  Presenting Final Year Project to Your Supervisor
Presenting Final Year Project to Your Supervisor  Trending Engineering Projects in 2024 Future-Ready
Trending Engineering Projects in 2024 Future-Ready  Innovative Renewable Energy Project Ideas
Innovative Renewable Energy Project Ideas  How Engineering Projects Ideas to contribute your academic year?
How Engineering Projects Ideas to contribute your academic year?  Latest Engineering Projects in 2024
Latest Engineering Projects in 2024  Ethical Considerations in Image Processing: Balancing Innovation and Privacy
Ethical Considerations in Image Processing: Balancing Innovation and Privacy  From Pixels to Insights A Journey into Image Enhancement Algorithms
From Pixels to Insights A Journey into Image Enhancement Algorithms 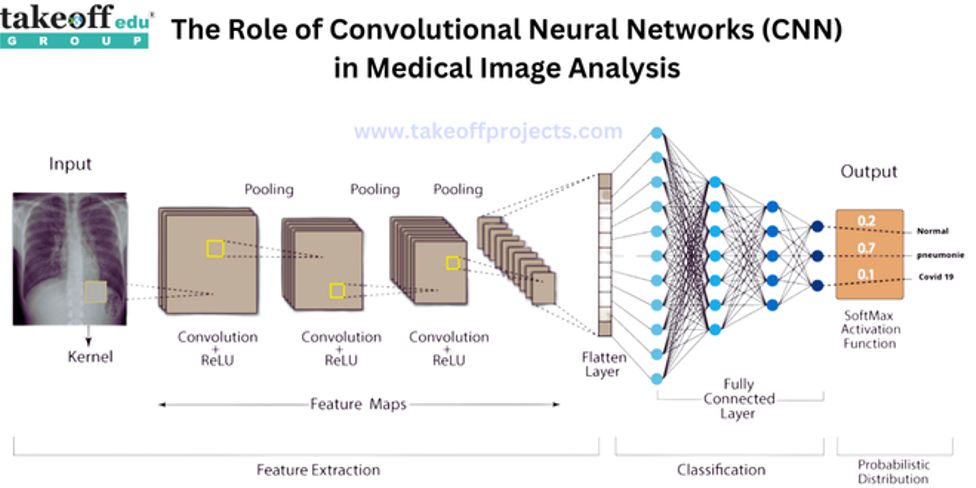 The Role of Convolutional Neural Networks in Medical Image Analysis
The Role of Convolutional Neural Networks in Medical Image Analysis  Advancements in Image Segmentation Techniques: A Comprehensive Overview
Advancements in Image Segmentation Techniques: A Comprehensive Overview 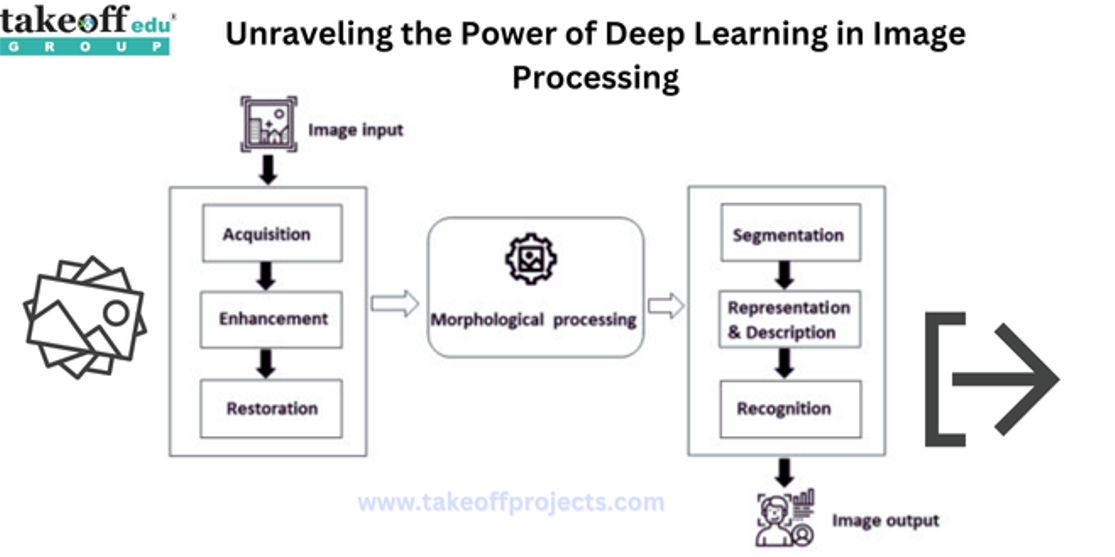 Unraveling the Power of Deep Learning in Image Processing
Unraveling the Power of Deep Learning in Image Processing  Importance of Final Year Projects for Students
Importance of Final Year Projects for Students  How to Present Your Final Year Project to Your Supervisor?
How to Present Your Final Year Project to Your Supervisor?  How to Choose the Right Final Year Project Topic?
How to Choose the Right Final Year Project Topic?  Common Mistakes to Avoid on Your Final Year Project
Common Mistakes to Avoid on Your Final Year Project  How to Write a Winning Engineering Project Report?
How to Write a Winning Engineering Project Report?  Low Cost Mini Projects Ideas for Civil Engineering
Low Cost Mini Projects Ideas for Civil Engineering  Low Cost Mini Project Ideas for Mechanical Engineering
Low Cost Mini Project Ideas for Mechanical Engineering  BSc IT Projects for Final Year
BSc IT Projects for Final Year  Instrumentation Projects for Final Year Students
Instrumentation Projects for Final Year Students  Biomedical Instrumentation Projects
Biomedical Instrumentation Projects  M.Tech Structural Engineering Projects
M.Tech Structural Engineering Projects  M.Tech Thesis Writing Services
M.Tech Thesis Writing Services  M.Tech Projects for Electrical, Electronics & Software Engineering
M.Tech Projects for Electrical, Electronics & Software Engineering  Latest Final Year Projects for B.Tech & M.Tech Students
Latest Final Year Projects for B.Tech & M.Tech Students  2023 B.Tech Final Year Projects for Students
2023 B.Tech Final Year Projects for Students  Latest BCA Final Year Project Ideas for 2023
Latest BCA Final Year Project Ideas for 2023  Top BE Projects Ideas & Topics for Students
Top BE Projects Ideas & Topics for Students  14+ Interesting Engineering Projects
14+ Interesting Engineering Projects  IEEE Final Year Projects
IEEE Final Year Projects 
 Paper Publishing
Paper Publishing


