Intelligent Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) Monitoring and Forecasting System
Objective
The objective of this project is to develop a machine learning model that accurately predicts the Air Quality Index (AQI Value), a numerical measure of overall air pollution levels. By utilizing key pollutant-specific AQI values such as CO, Ozone, NO?, and PM2.5 as input features, the model aims to forecast the final AQI value through a regression approach. This helps in proactive air quality monitoring and public health decision-making. The system can also be adapted for classification tasks (e.g., predicting AQI Category) to categorize air quality levels, enhancing its applicability in both analytical and alert-based environmental systems
Abstract
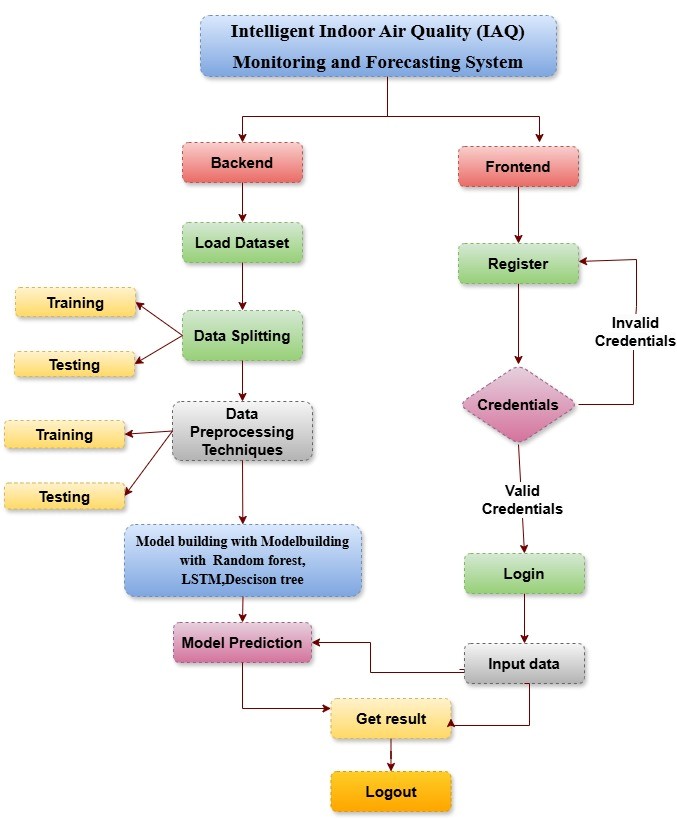
Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) has emerged as a crucial determinant of health and cognitive performance, especially in enclosed public spaces like hospitals and academic institutions. This project presents an intelligent IAQ monitoring and forecasting system that combines IoT-based environmental sensing, complex event processing (CEP), and advanced machine learning techniques. The system captures real-time measurements of pollutants such as carbon dioxide (CO₂), particulate matter (PM2.5), and total volatile organic compounds (TVOCs), along with temperature and humidity, using custom-built IoT sensor units installed across university lecture rooms. The processed sensor data is analyzed to perform two core predictive tasks: regression to forecast the Air Quality Level (AQL) as a continuous value, and classification to determine the AQL category (e.g., Good, Moderate, Unhealthy). Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks are used for temporal pattern learning, while Random Forest demonstrated superior accuracy in AQL regression tasks, offering robust generalization across varying conditions. For classification, Decision Tree Classifier outperformed other models, providing clear rule-based insights for pollution category identification. The CEP engine enables real-time pattern recognition and anomaly detection in sensor streams. By leveraging accurate predictions and interpretable classifications, the system supports proactive decisions on ventilation control and health safety. The framework offers a scalable approach to intelligent building management through the fusion of environmental sensing, predictive analytics, and actionable insights.
Keywords : Indoor Air Quality, Air Quality Level, IoT Sensors, Regression, Classification, Decision Tree, Random Forest, LSTM, PM2.5, CO₂, Complex Event Processing, AQL Forecasting, Environmental Analytics, Smart Building
NOTE: Without the concern of our team, please don't submit to the college. This Abstract varies based on student requirements.
Block Diagram






 Paper Publishing
Paper Publishing
