Evaluation of Feature Selection Using Machine Learning for Cyber-Attack Detection in Smart Grid
Objective
This project reviews feature selection techniques to improve machine learning models for detecting cyber-attacks in smart grids, aiming to enhance security, efficiency, and resilience of critical energy infrastructure.
Abstract
This review explores the evaluation of feature selection techniques using machine learning for detecting cyber-attacks in smart grids. As smart grids integrate advanced technologies to enhance power distribution and management, they become more susceptible to cyber threats. Effective feature selection is crucial to improve the performance of machine learning models in identifying these threats. This study analyzes various feature selection methods, including filter, wrapper, and embedded approaches, and their impact on model accuracy, precision, and recall. By reviewing recent research, we highlight the strengths and limitations of different techniques and suggest best practices for their application in smart grid cybersecurity. Our findings aim to guide future research and development in enhancing the resilience of smart grids against cyber-attacks.
NOTE: Without the concern of our team, please don't submit to the college. This Abstract varies based on student requirements.
Block Diagram
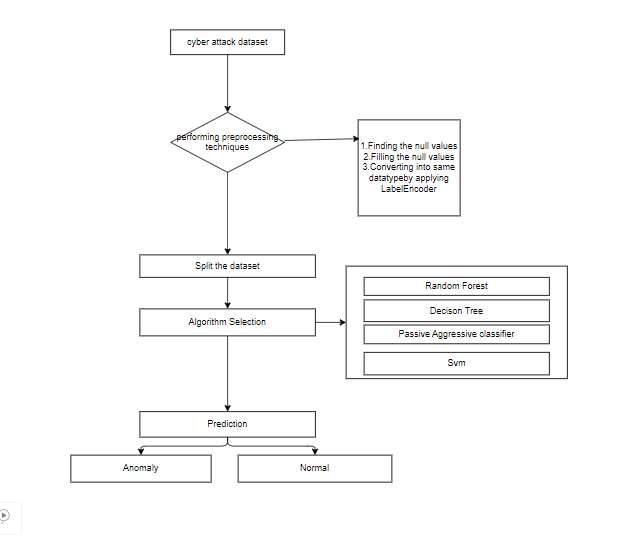
Specifications
H/W CONFIGURATION:
Processor - I3/Intel Processor
Hard Disk - 160GB
Key Board - Standard Windows Keyboard
Mouse - Two or Three Button Mouse
Monitor - SVGA
RAM - 8GB
S/W CONFIGURATION:
• Operating System : Windows 7/8/10
• Server side Script : HTML, CSS, Bootstrap & JS
• Programming Language : Python,Machinelearning
• Libraries : Flask, Pandas, Mysql.connector, Os, Scikit-learn, Numpy
• IDE/Workbench : PyCharm
• Technology : Python 3.6+
• Server Deployment : Xampp Server






 Paper Publishing
Paper Publishing
