SAM: A Segmentation based Approximate Multiplier for Error Tolerant Applications
Also Available Domains Arithmetic Core|Xilinx Vivado
Project Code :TVMATO761
Abstract
In this project, we propose a novel technique to
multiply two unsigned binary numbers through a Segmentation based Approximate
Multiplier (SAM). Approximate multiplier architectures face a fundamental
challenge, i.e to reduce the area and delay significantly without introducing
large inaccuracies. Almost all the existing approximate multipliers partition
the input operands to exploit parallelism in the flow. The proposed design
reduces the size of the Partial Products Matrix (PPM) in the order of n × (2n −
1) to a Reduced Partial Product Matrix (R-PPM) of the order 4 × 2n.
Additionally, it also eliminates the extra hardware required for compression
and rearrangement of partial products. µ-SAM, an optimized version of our basic
design is also proposed along with this work. µ-SAM further minimizes the area
and power consumption of the basic design.
NOTE: Without the concern of our team, please don't submit to the college. This Abstract varies based on student requirements.
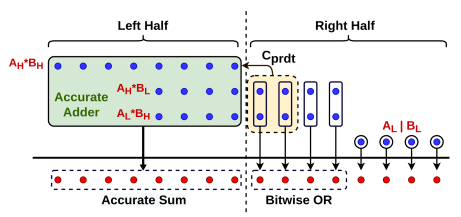
Block Diagram
Specifications
Software Requirements:
- Xilinx ISE Tool
- HDL: Verilog
Hardware Requirements:
- Microsoft® Windows XP,
- Intel® Pentium® 4 processor or Pentium 4 equivalent with SSE support
- 512 MB RAM
- 100 MB of available disk space
Learning Outcomes
- Basics of Digital Electronics
- VLSI design Flow
- Introduction to Verilog Coding
- Different modeling styles in Verilog
- Data Flow modeling
- Structural modeling
- Behavioral modeling
- Mixed level modeling
- Introduction to multiplier design
- About Dadda multiplication
- Knowledge on partial product generation and reduction
- Knowledge on adders, compressors
- About approximation computing
- Applications in real time
- Xilinx ISE 14.7 for design and simulation
- Generation of Netlist
- Solution providing for real time problems
- Project Development Skills:
- Problem Analysis Skills
- Problem Solving Skills
- Logical Skills
- Designing Skills
- Testing Skills
- Debugging Skills
- Presentation Skills
- Thesis Writing Skills
Demo Video
Related Topics


 Paper Publishing
Paper Publishing
