Joint Path Selection and Rate Allocation Framework for 5G Self-Backhauled mmWave Networks
Objective
The main objective of this project is to find the best suitable path for data transmission and to build an algorithm to allocate rate for the users for increment in data rate.
Abstract
In this project, a new system design, which exploits multiple antenna diversity, mmWave bandwidth, and traffic splitting techniques, is proposed to improve the downlink transmission. The studied problem is cast as a network utility maximization, subject to an upper delay bound constraint, network stability and network dynamics.
By leveraging stochastic optimization, the problem is decoupled into: (i) path selection and (ii) rate allocation sub-problems, whereby a framework which selects the best paths is proposed using reinforcement learning techniques. Moreover, the rate allocation is a non-convex program, which is converted into a convex one by using the successive convex approximation method. In this method, furthermore, the results showcase the key trade-off between latency and network arrival rate.
Keywords: Ultra-low latency and reliable communication (URLLC), self-backhaul, mmWave communications, multi-hop scheduling, ultra-dense small cells, stochastic optimization, reinforcement learning.
NOTE: Without the concern of our team, please don't submit to the college. This Abstract varies based on student requirements.
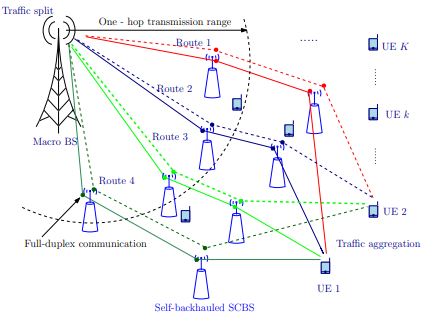
Block Diagram
Specifications
Software: Matlab 2018a or above
Hardware:
Operating Systems:
- Windows 10
- Windows 7 Service Pack 1
- Windows Server 2019
- Windows Server 2016
Processors:
Minimum: Any Intel or AMD x86-64 processor
Recommended: Any Intel or AMD x86-64 processor with four logical cores and AVX2 instruction set support
Disk:
Minimum: 2.9 GB of HDD space for MATLAB only, 5-8 GB for a typical installation
Recommended: An SSD is recommended A full installation of all Math Works products may take up to 29 GB of disk space
RAM:
Minimum: 4 GB
Recommended: 8 GB
Learning Outcomes
- Introduction to Matlab
- What is EISPACK & LINPACK
- How to start with MATLAB
- About Matlab language
- Matlab coding skills
- About tools & libraries
- Application Program Interface in Matlab
- About Matlab desktop
- How to use Matlab editor to create M-Files
- Features of Matlab
- Basics on Matlab
- Basics of wireless communications
- About rate allocation frame work
- How system modal can be formed in Matlab.
- Construction of algorithm according to system modal
- Analyzing and visualization of plots.
- Phases of data transmission:
- Generation of input signal
- Construction of transmitter
- Formation of channel
- Construction of receiver
- How to extend our work to another real time applications
- Project development Skills:
- Problem analyzing skills
- Problem solving skills
- Creativity and imaginary skills
- Programming skills
- Deployment
- Testing skills
- Debugging skills
- Project presentation skills
- Thesis writing skills





 Paper Publishing
Paper Publishing
