Area and Power Efficient VLSI Architecture of Distributed Arithmetic Based LMS Adaptive Filter
Objective
This paper presents a new area and power efficient VLSI architecture for least-mean-square (LMS) adaptive filterusing distributed arithmetic (DA).
Abstract
This paper presents a new area and power efficient VLSI architecture for least-mean-square (LMS) adaptive filterusing distributed arithmetic (DA). Conventionally, DA basedLMS adaptive filter requires look-up tables (LUTs) for filteringand weight updating operations. The size of LUTs grows exponentially with filter order. The proposed scheme has reducedthe LUT size to half by storing the offset-binary-coding (OBC) combinations of filter weights and input samples. To make theadaptive filter more area and power efficient, it is not necessary todecompose LUT into two smaller LUTs. Hence, by using the nondecomposed LUT the proposed design achieves significant savingsin area and power over the best existing scheme. In addition, the proposed architecture involves comparatively lesser hardwarecomplexity for the same LUT-size.
NOTE: Without the concern of our team, please don't submit to the college. This Abstract varies based on student requirements.
Block Diagram
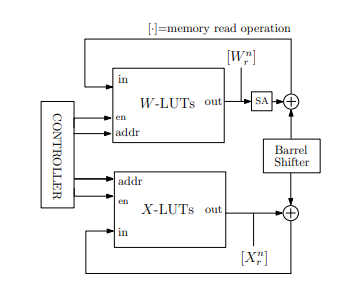
Specifications

Contact Us
- info@takeoffprojects.com
- +91 9030333433, +91 9393939065





 Paper Publishing
Paper Publishing
