Virtex 7 FPGA Implementation of 256 Bit Key AES Algorithm with Key Schedule and Sub Bytes Block Optimization
Also Available Domains Communications|Xilinx Vivado
Objective
The main objective of this paper is to improve the security by extending the cipher key size into 256 bit key AES algorithm and applied selective transformation for optimization.
Abstract
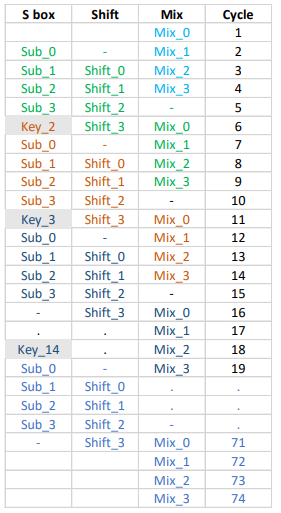
Information security has a major role in the development next generation communication system, where more randomization in the secret key is required for improved security without adding any complexity over existing cryptography algorithms. In the recent years Symmetric key algorithms like Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is widely used in many network security applications. In this paper we are proposing 256-bit AES algorithm is highly optimized in Key schedule and Sub bytes blocks, for Area and Power. The optimization has been done by reusing the S-box block. We are optimizing the algorithm with a new approach where internal operations are 32-bit operations, as compared to 128-bit operations. The proposed implementation helps in re-using the same hardware in a pipelined fashion which results in an area reduction by using slice registers. This in turn results in a power reduction in a FPGA implementation. The throughput (Mbps) of the proposed implementation using Virtex-7 (xc7vx485tffg1157) FPGA improved.
Keywords: Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), FPGA, LUT (Look up table), Mbps (megabit per second), sub (sub bytes), shift (shift rows), mix (mix column), add (add round key).
NOTE: Without the concern of our team, please don't submit to the college. This Abstract varies based on student requirements.
Block Diagram
Specifications
Software Requirements:
- Xilinx ISE Tool
- HDL: Verilog
Hardware Requirements:
- Microsoft® Windows XP,
- Intel® Pentium® 4 processor or Pentium 4 equivalent with SSE support
- 512 MB RAM
- 100 MB of available disk space
Learning Outcomes
- Basics of Digital Electronics
- FPGA design Flow
- Introduction to Verilog Coding
- Different modeling styles in Verilog
- Data Flow modeling
- Structural modeling
- Behavioral modeling
- Mixed level modeling
- Concept of Cryptography systems
- Importance of Crypto systems
- Drawbacks of existing methods
- Introduction to Advanced Encryption standard (AES)
- Knowledge on pipelining concept
- Knowledge on Symmetric, Asymmetric and Hash functions
- Applications of AES in real time
- Scope of AES concept in today’s world
- Applications in real time
- Xilinx ISE 14.7 for design and simulation
- Generation of Netlist
- Solution providing for real time problems
- Project Development Skills:
- Problem Analysis Skills
- Problem Solving Skills
- Logical Skills
- Designing Skills
- Testing Skills
- Debugging Skills
- Presentation Skills
- Thesis Writing Skills


 Paper Publishing
Paper Publishing
