RGB Image Compression Using Discrete Cosine Transform Algorithm
Objective
This study computes the two-dimensional DCT of 8-by-8 blocks in an input image, dismisses all but 10 of the DCT coefficients in each block, and afterwards reconstructs the image using the two-dimensional inverse DCT of each block." Transform matrices are used in the computing process.
Abstract
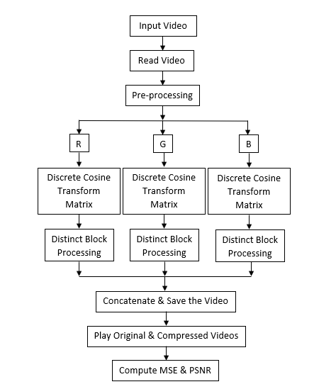
This main objective of this work is to compress an image/video using the Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT). Naturally, JPEG image compression algorithm uses DCT to compress images. When the DCT is computed, the image is split into 8x8 or 16x16 blocks whereas in videos, frames will be considered.
As a result of these steps, the DCT coefficients are then quantized, coded, and then sent. As soon as the quantized DCT coefficients are decoded, the JPEG receiver (or JPEG file reader) computes each block's two-dimensional inverse DCT, and then combines the blocks into a single image.
he values of several of the DCT coefficients for common images are close to zero. In the absence of these coefficients, the image reconstruction may be done without compromising its quality in any way.
Keywords: Discrete Cosine Transform, Image Compression, 2-D Inverse DCT, Image Reconstruction
NOTE: Without the concern of our team, please don't submit to the college. This Abstract varies based on student requirements.
Block Diagram
Specifications
Software: Matlab 2020a or above
Hardware:
Operating Systems:
- Windows 10
- Windows 7 Service Pack 1
- Windows Server 2019
- Windows Server 2016
Processors:
Minimum: Any Intel or AMD x86-64 processor
Recommended: Any Intel or AMD x86-64 processor with four logical cores and AVX2 instruction set support
Disk:
Minimum: 2.9 GB of HDD space for MATLAB only, 5-8 GB for a typical installation
Recommended: An SSD is recommended A full installation of all MathWorks products may take up to 29 GB of disk space
RAM:
Minimum: 4 GB
Recommended: 8 GB
Learning Outcomes
- Introduction to Matlab
- What is EISPACK & LINPACK
- How to start with MATLAB
- About Matlab language
- Matlab coding skills
- About tools & libraries
- Application Program Interface in Matlab
- About Matlab desktop
- How to use Matlab editor to create M-Files
- Features of Matlab
- Basics on Matlab
- What is an Image/pixel?
- About image formats
- Introduction to Image Processing
- How digital image is formed
- Importing the image via image acquisition tools
- Analyzing and manipulation of image.
- Phases of image processing:
- Acquisition
- Image enhancement
- Image restoration
- Color image processing
- Image compression
- Morphological processing
- Segmentation etc.,
- About Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- About Machine Learning
- About Deep Learning
- About layers in AI (input, hidden and output layers)
- Building AI (ANN/CNN) architecture using Matlab
- We will able to know, what’s the term “Training” means in Artificial Intelligence
- About requirements that can influence the AI training process:
- Data
- Training data
- Validation data
- Testing data
- Hardware requirements to train network
- How to detect an object using AI
- How to extend our work to another real time applications
- Project development Skills
- Problem analyzing skills
- Problem solving skills
- Creativity and imaginary skills
- Programming skills
- Deployment
- Testing skills
- Debugging skills
- Project presentation skills
- Thesis writing skills





 Paper Publishing
Paper Publishing
