Grid-Forming Control for Solar PV Systems with Power Reserves
Objective
The main objective of this project is to Reactive Power Synchronization Method for Renewable Power Plants
Abstract
The massive penetration of renewable energy sources in electrical systems has been displacing synchronous generators (SGs) from conventional power plants in the last few years. Renewable generation plants are usually connected to power grids through electronic power converters, which cannot provide the same power generation services as SGs due to their mode of operation. Recently, different concepts have been proposed for electronic converter control in an attempt to emulate the performance of SGs, resulting in the so-called grid-forming converters (GFCs).
This paper proposes a new GFC control strategy based on the reactive power synchronization (RPS) method, which decouples the synchronizing power and the active power control of renewable generation source to which a converter is connected. For this purpose, this study assesses three power sources: batteries, photovoltaic (PV) plants, and full-converter wind turbines. Moreover, the study proposes models and controls for each of these sources, whose dynamics exert a decisive influence on the grid services provided by renewable energy plants. Thereafter, the study proposes a GFC–RPS control scheme and verifies its effectiveness in different applications; for example, inertial response, which provides power immediately through a fast frequency response after a grid has experienced a load variation. Unlike storage systems and wind turbines, PV plants can only render these services if they are not operating at maximum power. Further, the study validates the GFC–RPS control strategy for regulating AC voltage at the output terminals of a converter. Finally, the paper assesses GFC hot swapping during the transition from a grid-connected to an isolated-operation mode while feeding a dynamic load. Results revealed that both the voltage and frequency remain stable, thereby demonstrating that the proposed GFC–RPS control indeed acts as a true voltage source and emulates the behaviour of a conventional SG.
INDEX TERMS- Grid-forming power converter, renewable energy sources, reactive power synchronization, fast frequency response, converter hot swapping.
NOTE: Without the concern of our team, please don't submit to the college. This Abstract varies based on student requirements.
Block Diagram
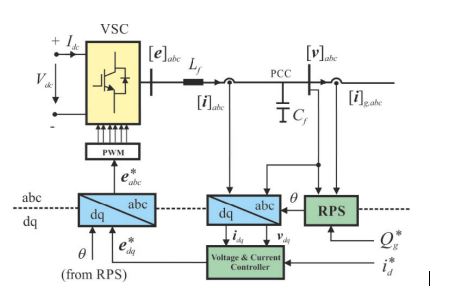
Specifications
Software Configuration:
Operating System : Windows 7/8/10
Application Software : Matlab/Simulink
Hardware Configuration:
RAM : 8 GB
Processor : I3 / I5(Mostly prefer)
Learning Outcomes
- Introduction to Matlab/Simulink
- What is EISPACK & LINPACK
- How to start with MATLAB
- About Matlab language
- About tools & libraries
- Application of Matlab/Simulink
- About Matlab desktop
- Features of Matlab/Simulink
- Basics on Matlab/Simulink
- Introduction to controllers.
- Study of PWM techniques.
- Project Development Skills:
- Problem analyzing skills
- Problem solving skills
- Creativity and imaginary skills
- Programming skills
- Deployment





 Paper Publishing
Paper Publishing
