Electricity Price Forecasting for Cloud Computing Using an Enhanced Machine Learning Model
Objective
In this project, we propose an Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) model to offload or move storage, predict electricity price. As a result reducing energy consumption costs in data centers. The performance of this method is evaluated on a real-world dataset.
Abstract
Cloud computing is rapidly taking over the information technology industry because it makes computing a lot easier without worries of buying the physical hardware needed for computations, rather, these services are hosted by companies with provide the cloud services. These companies contain a lot of computers and servers whose main source of power is electricity, hence, design and maintenance of these companies is dependent on the availability of steady and cheap electrical power supply.
Cloud centers are energy-hungry. With recent spikes in electricity prices, one of the main challenges in designing and efficient data placement and node scheduling to offload or move storage are some of the maintenance of such centers is to minimize electricity consumption of data centers and save energy. Ein approaches to solve these problems.
In this project, we propose an Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) model to offload or move storage, predict electricity price, and as a result reduce energy consumption costs in data centers. The performance of this method is evaluated on a real-world dataset provided by the Independent Electricity System Operator (IESO) in Ontario, Canada, to offload data storage in data centers and efficiently decrease energy consumption. The data is split into 70% training and 30% testing.
Keywords: Data Storage, Energy Saving, Electricity Price Forecasting, XGBoost.
NOTE: Without the concern of our team, please don't submit to the college. This Abstract varies based on student requirements.
Block Diagram
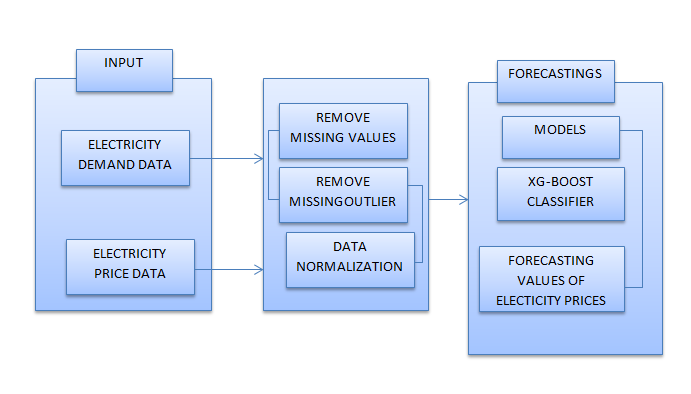
Specifications
HARDWARE SPECIFICATIONS:
- Processor: I3/Intel
- Processor RAM: 4GB (min)
- Hard Disk: 128 GB
- Key Board: Standard Windows Keyboard
- Mouse: Two or Three Button Mouse
- Monitor: Any
SOFTWARE SPECIFICATIONS:
- Operating System: Windows 7+
- Server-side Script: Python 3.6+
- IDE: PyCharm
- Libraries Used: Pandas, Numpy, os, sklearn, Pillow, TensorFlow.
Learning Outcomes
- Scope of real time application scenarios.
- Objective of the project.
- How Internet Works.
- What is a search engine and how browser can work.
- What type of technology versions are used.
- Use of HTML , and CSS on UI Designs.
- Data Parsing Front-End to Back-End.
- Working Procedure.
- Introduction to basic technologies used for.
- How project works.
- Input and Output modules.
- Frame work use.
- About python.
- What is machine learning?
- What are machine learning algorithms?
- How can we identify and detect the fake reviews by using machine learning algorithms.
- How can we classify good reviews and fake reviews?
- What is meant by preprocessing?
- What are preprocessing techniques?
- How this forecasting is helpful in electricity price prediction.
- What is machine learning?
- Machine learning algorithms.
- What is XgBoost.
- How gradient boosting works.
- Project Development Skills:
- Problem analyzing skills.
- Problem solving skills.
- Creativity and imaginary skills.
- Programming skills.
- Deployment.
- Testing skills.
- Debugging skills.
- Project presentation skills.
- Thesis writing skills.





 Paper Publishing
Paper Publishing
