Election Exit Poll Prediction
Objective
Predicting election results is a hot field of political science. In the last decade, social media has been commonly used in democratic campaigns. The results of a national election can be predicted by most techniques.
Abstract
Predicting the ultimate outcomes of certain municipal elections is still difficult. This app introduces a technique focused on machine learning for analyzing data to predict the ultimate outcomes of many local elections. The proliferation of social media in the recent past has provided end users a powerful platform to voice their opinions. Businesses need to identify the polarity of these opinions in order to understand user orientation and thereby make smarter decisions. One such application is in the field of politics, where political entities need to understand public opinion and thus determine their campaigning strategy.
Sentiment analysis on social media data has been seen by many as an effective tool to monitor user preferences and inclination. Popular text classification algorithms like Naive Bayes and SVM are Supervised Learning Algorithms which require a training data set to perform Sentiment analysis. The accuracy of these algorithms is contingent upon the quantity as well as the quality of the labelled training data. Since most applications suffer from lack of training data, they resort to cross domain sentiment analysis which misses out on features relevant to the target data. This, in turn, takes a toll on the overall accuracy of text classification.
Keywords: Election Poll, Prediction, Mood Sensing, Naïve Bayes, SVM.
NOTE: Without the concern of our team, please don't submit to the college. This Abstract varies based on student requirements.
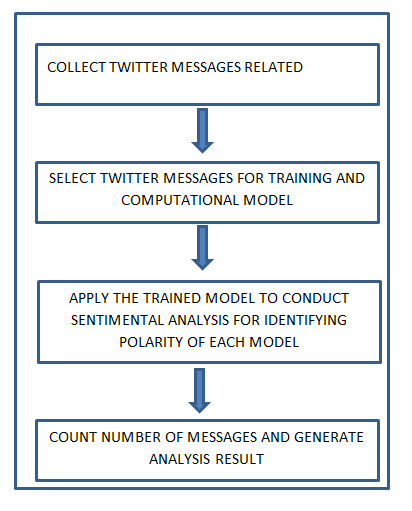
Block Diagram
Learning Outcomes
- Scope of predicting the election result.
- What is twitter data.
- How to collect data from sources.
- How to prepress data.
- Real time application scenarios.
- Create the model.
- How model can train.
- How ML can work and real time applications.
- Working of SVM.
- Android architecture.
- Basic about java.
- Basic about MySQL.
- Knowledge about server side programming.
- Difference between client side and server side programming language.
- Knowledge about server.
- Knowledge about database and queries.
- Knowledge about Volley API.
- How to communicate with API.
- How API Communicate with Server.
- What are Packages and dependencies regarding the app?
- What are various versions of android app and android operating system.
- About Android studio.
- Client side validation.
- Server side validation.
- Difference between client side validations.
- Different Debugging Techniques.
- Deployment of app.
- About play store deployment.
- What is manifest?
- About XML.
- Widgets in android.
- Views in android.
- Layouts in android.
- How to design the user Interface.
- Project Development Skills:
- Problem analyzing skills.
- Problem solving skills.
- Creativity and imaginary skills.
- Programming skills.
- Deployment.
- Testing skills.
- Debugging skills.
- Project presentation skills.
- Thesis writing skills.






 Paper Publishing
Paper Publishing
