Efficient Cell-Specific Beamforming For Large Antenna Arrays
Objective
An efficient method for designing broadbeams with spatially flat array factor and efficient power utilization for cell-specific coverage in communication systems equipped with large antenna arrays is proposed.
Abstract
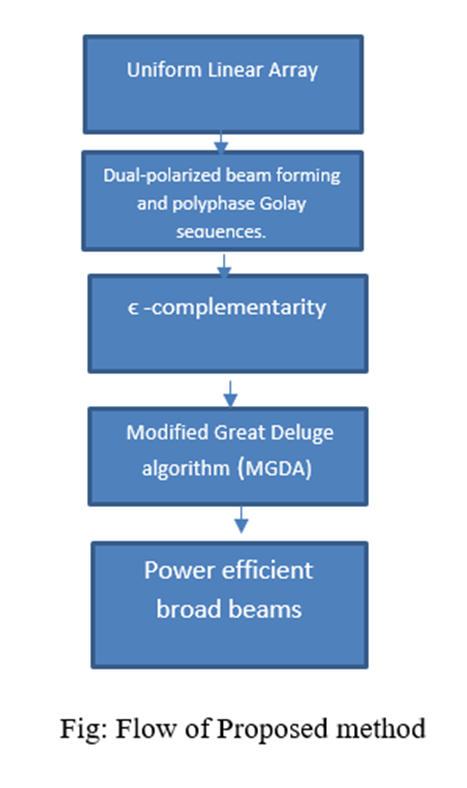
We propose an efficient method for designing broad beams with spatially flat array factor and efficient power utilization for cell-specific coverage in communication systems equipped with large antenna arrays. To ensure full power efficiency, the method is restricted to phase-only weight manipulations. Our framework is based on the discovered connection between dual-polarized beam forming and polyphone Golay sequences. Exploiting this connection, we propose several methods for array expansion from smaller to larger sizes, while preserving the radiation pattern. In addition, to fill the gaps in the feasible array sizes, we introduce the concept of ϵ-complementarity that relaxes the requirement on zero side lobes of the sum aperiodic autocorrelation function of a sequence pair. Furthermore, we develop a modified Great Deluge algorithm (MGDA) that finds ϵ-complementary pairs of arbitrary length, and hence enables broad beam forming for arbitrarily-sized uniform linear arrays. We also discuss the extension of this approach to two-dimensional uniform rectangular arrays. Our numerical results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed approach with respect to existing beam-broadening methods.
Index Terms—Beam forming, MIMO systems, control channel, broad beams, complementary sequences.
NOTE: Without the concern of our team, please don't submit to the college. This Abstract varies based on student requirements.
Block Diagram
Specifications
Software & Hardware Requirements:
Software: Matlab 2018a or above
Hardware:
Operating Systems:
- Windows 10
- Windows 7 Service Pack 1
- Windows Server 2019
- Windows Server 2016
Processors:
Minimum: Any Intel or AMD x86-64 processor
Recommended: Any Intel or AMD x86-64 processor with four logical cores and AVX2 instruction set support
Disk:
Minimum: 2.9 GB of HDD space for MATLAB only, 5-8 GB for a typical installation
Recommended: An SSD is recommended a full installation of all Math Works products may take up to 29 GB of disk space
RAM:
Minimum: 4 GB
Recommended: 8 GB
Learning Outcomes
- Introduction to Matlab
- What is EISPACK & LINPACK
- How to start with MATLAB
- About Matlab language
- Matlab coding skills
- About tools & libraries
- Application Program Interface in Matlab
- About Matlab desktop
- How to use Matlab editor to create M-Files
- Features of Matlab
- Basics on Matlab
- Basics of wireless sensor networks
- About Leach protocols.
- How system modal can be formed in Matlab.
- Construction of algorithm according to system modal
- Analyzing and visualization of plots.
- About WSN lifetimes.
- About cluster heads and aggregators.
- About data transmission in-between nodes.
- Phases of data transmission:
- Generation of input data
- Construction of WSN nodes
- How to extend our work to another real time applications
- Project development Skills
- Problem analyzing skills
- Problem solving skills
- Creativity and imaginary skills
- Programming skills
- Deployment
- Testing skills
- Debugging skills
- Project presentation skills
- Thesis writing skills





 Paper Publishing
Paper Publishing
