Design of Delay Efficient Hybrid Adder for High Speed Applications
Objective
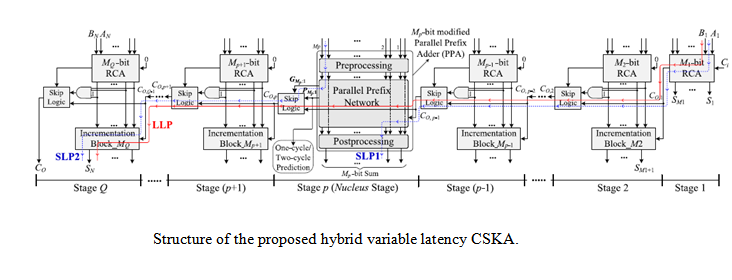
Hardware description language (HDL) is used to describe the functionality of the system. To effectively implement this adder we use the concept of “Hybrid Variable Latency” technique.
Abstract
Complex processor system design is partitioned into smaller sub-systems. These subsystems consist of circuits such as the adder, subtractor, multiplier, and functional units. Adders are the elementary building block in these arithmetic subsystems. Arithmetical and Logical Unit (ALU) is an essential component in CPU. Processing speed in CPU depends upon the time taken for processing a data. In the critical path of arithmetic subsystems, the main components are adders. The important metric for measuring the quality of adders is the critical-path delay, number of logic levels and area. Improving the speed without compromising the power is of greater concern. Thus, there is a need for an energy-efficient, low-power, and high-performance architecture. In this paper, a modified approach is presented to address this issue. The design employed utilizes the advantage of parallel prefix architecture (PPA) design for low power applications. Hardware description language (HDL) is used to describe the functionality of the system. To effectively implement this adder we use the concept of “Hybrid Variable Latency” technique. The Performance parameters of the adder are reported using Cadence tool (RTL-Compiler) in 45-nm technology and functionality of the design is validated using Vivado HLS. In comparison with the existing techniques, the proposed scheme is relatively faster and also it shows improvement in delay by 7.19% and 15.63% respectively.
NOTE: Without the concern of our team, please don't submit to the college. This Abstract varies based on student requirements.
Block Diagram
Specifications

Contact Us
- info@takeoffprojects.com
- +91 9030333433, +91 9393939065





 Paper Publishing
Paper Publishing
