Beyond 5G: Reducing the Handover Rate for High Mobility Communications
Objective
Developing proximity-based clusters utilizing hierarchical partitioning can enhance nomadic cell formation for handling high handover rates in dense 5G and beyond networks, addressing scalability, real-time constraints, and pragmatic challenges overlooked by prior schemes.
Abstract
A
vast number of mobile devices are anticipated to be supported by cellular
networks that are fifth generation (5G) and beyond, allowing them to move effortlessly
across minuscule cells. As a result, a very high handover rate is anticipated
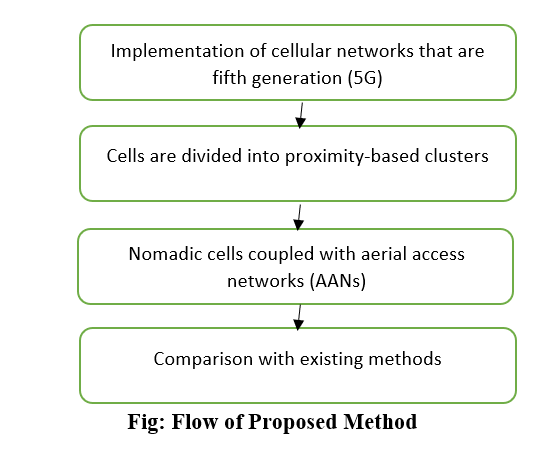
for these incredibly dense networks. According to this study, proximity-based
clusters can be employed as nomadic cells coupled with aerial access networks
(AANs) to handle a large number of highly mobile devices in 5G and beyond
networks and lessen the load generated by quick handover requests. The mobile
devices are divided into proximity-based clusters using a two-level
hierarchical partitioning technique to generate these nomadic cells. Earlier
distributed mobility management systems aren't effective enough to handle the
handover rate anticipated for networks running 5G and beyond. Previous
group-based approaches are not suitable for real-time applications due to their
high computational complexity. The suggested method, in contrast to
conventional schemes, scales with the quantity of devices. Furthermore, the
establishment of a mobility group brings up pragmatic challenges that prior
schemes ignored, in addition to security and privacy concerns.
This study addresses these difficulties.
Keywords: 5G and Beyond Networks, Aerial Access Networks, Cellular Networks, Mobility Management.
NOTE: Without the concern of our team, please don't submit to the college. This Abstract varies based on student requirements.
Block Diagram
Specifications
Software: Matlab 2020a or above
Hardware:
Operating Systems:
- Windows 10
- Windows 7 Service Pack 1
- Windows Server 2019
- Windows Server 2016
Processors:
Minimum: Any Intel or AMD x86-64 processor
Recommended: Any Intel or AMD x86-64 processor with four logical cores and AVX2 instruction set support
Disk:
Minimum: 2.9 GB of HDD space for MATLAB only, 5-8 GB for a typical installation
Recommended: An SSD is recommended A full installation of all MathWorks products may take up to 29 GB of disk space
RAM:
Minimum: 4 GB
Recommended: 8 GB
Learning Outcomes
· Introduction to Matlab
· What is EISPACK & LINPACK
· How to start with MATLAB
· About Matlab language
· Matlab coding skills
· About tools & libraries
· Application Program Interface in Matlab
· About Matlab desktop
· How to use Matlab editor to create M-Files
· Features of Matlab
· Basics on Matlab
· What is Communication?
· About Communication
· Introduction to Communication
· How Communication Works?
· Importing the System Design, Characterization and Visualization
· Analyzing of BER tool
· Analyzing of Error Rate Test Console
· Generation of WSN
· WSN network creation
· Nodes Communication
· Clustering
· Routing
· Convolutional
· Equalization and Synchronization etc.,
· How to extend our work to another real time applications
· Project development Skills
o Problem analyzing skills
o Problem solving skills
o Creativity and imaginary skills
o Programming skills
o Deployment
o Testing skills
o Debugging skills
o Project presentation skills
o Thesis writing skills





 Paper Publishing
Paper Publishing
