Attribute-hiding Predicate Encryption With Equality Test In Cloud Computing
Abstract
Attribute-hiding Predicate Encryption with Equality Test in Cloud Computing
Abstract
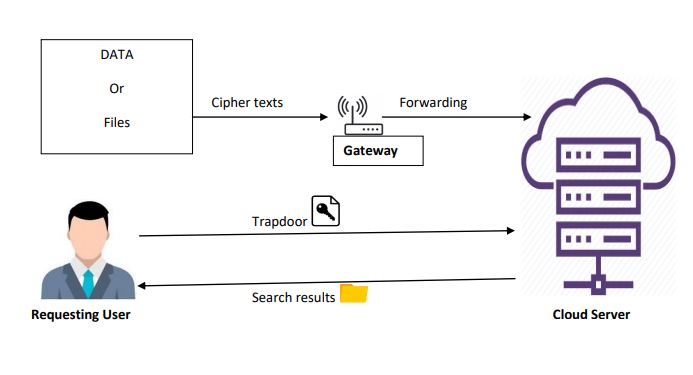
Cloud computing is an on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage and computing power, without direct active management by the user. The term is generally used to describe data centers available to many users over the Internet. Previously “partially hiding” predicate encryption scheme for functions that compute an arithmetic branching program on public attributes followed by an inner product predicate on private attributes. This constitutes the first “best of both worlds” result in bilinear groups that simultaneously generalizes existing attribute-based encryption schemes and inner product predicate encryption. Now Public key encryption with equality test (known as PKE-ET) enables anyone to perform equivalence test between two messages encrypted under distinct public keys. Attribute-hiding predicate encryption is a paradigm for public key encryption that supports both attribute-hiding and fine-grained access control. In this paper, we first initialize the concept of attribute-hiding predicate encryption with equality test (shorten as AH-PE-ET) by incorporating the notions of PKE-ET and PE, and then propose a concrete AH-PE-ET scheme. Inheriting the merits of predicate encryption, versatile access control can be achieved such that the cipher texts and the secret key are respectively associated with the descriptive attributes x and the Boolean functions f and decryption can only be done if f(x) returns true. In the AH-PE-ET scheme, one data receiver can calculate a trapdoor using his/her private key and deliver this trapdoor to an un-trusted cloud server, who in turn compares the cipher texts from this receiver with other receivers’ cipher texts
NOTE: Without the concern of our team, please don't submit to the college. This Abstract varies based on student requirements.
Block Diagram






 Paper Publishing
Paper Publishing
