Approximate Adiabatic Logic for Low-Power and Secure Edge Computing
Also Available Domains Low Power VLSI|Cadence EDA
Project Code :TVPGTO639
Objective
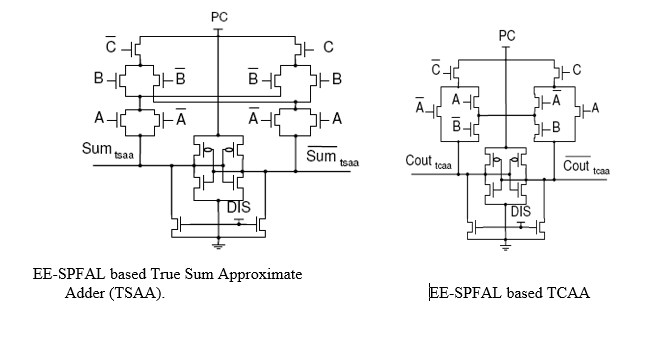
This paper aims to implement a full adder sum circuit and carry circuit is designed using Energy-Efficient Secure Positive Feedback Adiabatic Logic (EE-SPFAL). Energy-Efficient Secure Positive Feedback Adiabatic Logic (EE-SPFAL) is an adiabatic logic family which is suitable to design low-power and secure adiabatic circuit. EE-SPFAL has uniform power consumption and is secure against Differential Power Analysis (DPA) based attacks.
Abstract
Approximate computing is a promising approach
for error-tolerant applications running on the Internet of Things (IoT) edge
devices to reduce power consumption. However, approximate computation is
susceptible to side-channel attacks, such as attacks based on differential
power analysis (DPA). Energy efficiency could be further enhanced by applying
adiabatic logic in approximate edge computing while increasing its protection
against the side-channel attacks. As a case study, we are presenting two
approximate adders TSAA & TCAA based on adiabatic logic to illustrate the
benefits of approximate computation combined with adiabatic logic. The proposed
approximate adders leverage the dual-rail property of adiabatic logic to
minimize the overall size and further decrease energy consumption. At some
operating frequency and 45 nm technology node, the adiabatic TSAA and TCAA
achieved power saving, energy saving in comparison with the standard CMOS AMA.
We also show that both designs proposed are more secure against DPA attacks.
NOTE: Without the concern of our team, please don't submit to the college. This Abstract varies based on student requirements.
Block Diagram
Specifications
Software Requirements:
- Tanner EDA
- Technology files: 45nm
Hardware Requirements:
- Microsoft® Windows XP
- Intel® Pentium® 4 processor or Pentium 4 equivalent with SSE support
- 512 MB RAM
- 100 MB of available disk space
Learning Outcomes
- Introduction to adiabatic logic and approximate computing
- Need of approximate computing and adiabatic logic in DSP applications
- Transistors & its applications
- Types of Transistors
- Logic Gates using Transistors
- Pull Up and Pull Down networks
- Importance of Transistors
- MOS Fundamentals
- NMOS/PMOS/CMOS Technologies
- How to design circuits using Transistor logic?
- Transistor level design for approximate adder.
- How to design low power, high speed area efficient transistor level circuits?
- Drawbacks in CMOS technology
- Scope of adiabatic logic and approximate computing in today’s world
- Applications in real time
- Tanner EDA tool for design and simulation
- Solution providing for real time problems
- Project Development Skills:
- Problem Analysis Skills
- Problem Solving Skills
- Logical Skills
- Designing Skills
- Testing Skills
- Debugging Skills
- Presentation skills
- Thesis Writing Skills
Related Topics





 Paper Publishing
Paper Publishing
