An Efficient Modified Distributed Arithmetic Architecture Suitable for FIR Filter
Also Available Domains Xilinx Vivado|DSP Core
Abstract
One of the essential components of a Digital Signal Processing (DSP) system is the Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filter. FIR filter uses the Multiply and Accumulate (MAC) operation for its computation. Conventional MAC units are slow and consume high power, making them unsuitable for energy constrained devices. The MAC operations in FIR filter uses constant filter coefficients as one of its inputs. This situation is well suited for a bit-serial technique such as Distributed Arithmetic (DA). However, the traditional DA has the drawback of using huge memory resources as the filter order increases. An efficient LUT-less Modified Distributed Arithmetic architecture is proposed in this paper to solve the memory problem. This architecture removes the need for pre-computation of weighted sums needed for the LUT in a DA using multiplexers and adders. Also, the architecture is designed to extend the range of input values. Further, a 16-Tap FIR filter is designed, synthesized with Xilinx ISE, and implemented for an XC4VSX35-FF668-10 based FPGA to measure the performance of this architecture. Our implementation results show that the design uses fewer resources and achieves faster filtering than the filter’s previous implementations.
Index Terms—Distributed Arithmetic, Multiply and Accumulate, FIR Filter, FPGA
NOTE: Without the concern of our team, please don't submit to the college. This Abstract varies based on student requirements.
Block Diagram
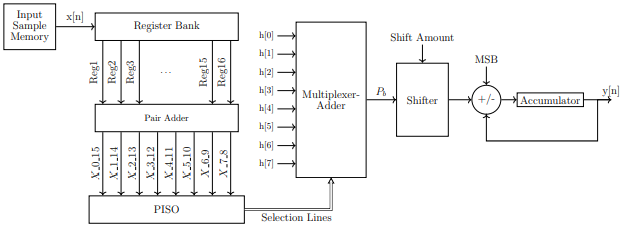
Specifications
Software Requirements:
- Xilinx ISE Tool
- HDL: Verilog
Hardware Requirements:
- Microsoft® Windows XP,
- Intel® Pentium® 4 processor or Pentium 4 equivalent with SSE support
- 512 MB RAM
- 100 MB of available disk space
Learning Outcomes
- Basics of Digital Electronics
- FPGA design Flow
- Introduction to Verilog Coding
- Different modeling styles in Verilog
- Data Flow modeling
- Structural modeling
- Behavioral modeling
- Mixed level modeling
- Concept of Distributed Arithmetic based Filter
- Importance of LUT less Distributed Arithmetic
- Drawbacks of LUT based Filters
- Introduction to Filters
- Knowledge on PISO unit, multiplier-adder unit, shifter unit, control unit.
- Applications of DA based filters in real time
- Scope of filters concept in today’s world
- Applications in real time
- Xilinx ISE 14.7 for design and simulation
- Generation of Netlist
- Solution providing for real time problems
- Project Development Skills:
- Problem Analysis Skills
- Problem Solving Skills
- Logical Skills
- Designing Skills
- Testing Skills
- Debugging Skills
- Presentation Skills
- Thesis Writing Skills





 Paper Publishing
Paper Publishing
