Active Fault Current Limitation for Low-Voltage Ride-Through of Networked Microgrids
Objective
The main objective of this project is to improve the voltage control ability of LVRT, the CCG strategy
Abstract
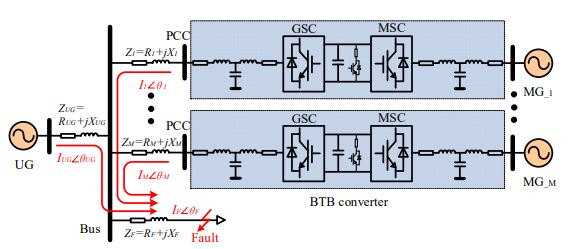
with the continuously increasing penetration of networked microgrids (MGs) on the local utility grid (UG), MGs face the challenge to avoid increasing system fault currents during low-voltage ride-through (LVRT). To solve this challenge, an active fault current limitation (AFCL) method is proposed with three parts: 1) a novel phase angle adjustment (PAA) strategy is conducted to relieve the impact of MGs output fault current on system fault current; 2) the current injection (CI) strategy for LVRT is formulated to fit the function of PAA; 3) a novel converter current generation (CCG) strategy is developed to achieve a better voltage support ability by considering network impedance characteristics.
The proposed AFCL method is applied to the back-to-back converter, as a connection interface between MGs and UG. Extensive tests and pertinent results have verified the improvements of proposed AFCL method with better LVRT performance, while the networked MGs output fault current does not increase the amplitude of system fault current.
Index Terms—Networked microgrids, back-to-back converter, low-voltage ride-through, fault current limitation.
NOTE: Without the concern of our team, please don't submit to the college. This Abstract varies based on student requirements.
Block Diagram
Specifications
Software Configuration:
Operating System : Windows 7/8/10
Application Software : Matlab/Simulink
Hardware Configuration:
RAM : 8 GB
Processor : I3 / I5(Mostly prefer)
Learning Outcomes
- Introduction to Matlab/Simulink
- What is EISPACK & LINPACK
- How to start with MATLAB
- About Matlab language
- About tools & libraries
- Application of Matlab/Simulink
- About Matlab desktop
- Features of Matlab/Simulink
- Basics on Matlab/Simulink
- Introduction to controllers.
- Study of PWM techniques.
- Project Development Skills:
- Problem analyzing skills
- Problem solving skills
- Creativity and imaginary skills
- Programming skills
- Deployment
- Testing skills
- Debugging skills
- Project presentation skills
- Thesis writing skills





 Paper Publishing
Paper Publishing
